How to increase the swap partition in Linux Mint and Ubuntu. How to create a Swap file in Linux
July 2, 2022
In this article, using Linux Mint and Ubuntu as an example, we will learn how to view information on the swap partition, create a swap file, and also increase the space available for swap.
The swap file is a specific place on permanent storage (for example, on a hard disk), where data that does not fit in RAM is temporarily dumped. That is, it is an opportunity to increase the amount of RAM without buying RAM modules. But such a “virtual” RAM is slower.
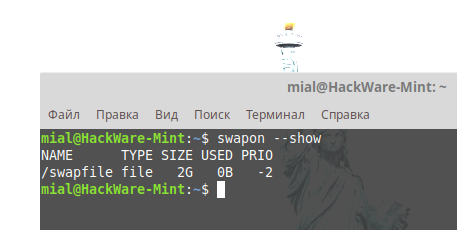
You can view the current size of the swap partition with the command:
swapon --show
Or with the free command:
free -h
Or with top:
top
As you can see, there is a 2 GB swap file on the system, which, let's say, is not enough.
Disable and delete this paging file with the following commands:
sudo swapoff -a sudo rm -f /swapfile
There must be enough space on the disk to fit the swap file of the size you specified.
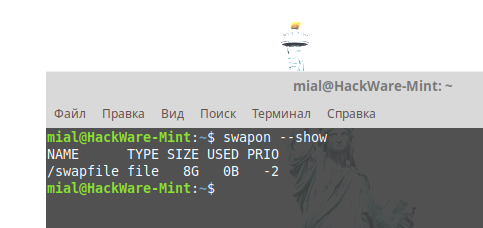
To create an 8G swap file (change the value as you wish) run the command:
sudo fallocate -l 8G /swapfile
Then run the commands:
sudo chmod 600 /swapfile sudo mkswap /swapfile sudo swapon /swapfile
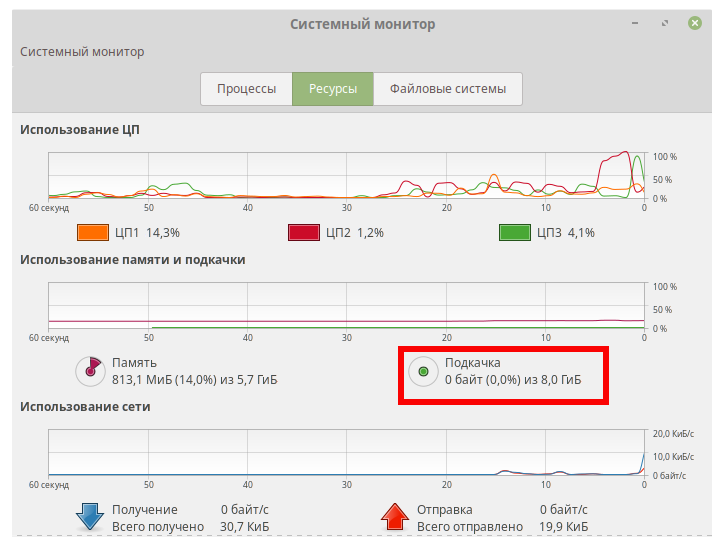
Open System Monitor to make sure the system uses the swap file:
Or you can do it with the command:
swapon --show
That's all! You don't even need to reboot your system for the changes to take effect.
By the way, if you go again to change the size of the paging file (up or down – it doesn’t matter), then exactly follow the same instructions again, but specify a different size when creating the paging file.
How to delete swap file in Linux Mint and Ubuntu
To completely remove the paging file, run the commands:
sudo swapoff -a sudo rm -f /swapfile
Then open the /etc/fstab file:
sudo gedit /etc/fstab
And remove the line from it:
/swapfile none swap defaults 0 0
Error “fallocate: fallocate failed: Text file busy”
If you encounter an error:
fallocate: fallocate failed: Text file busy
This means that you want to create a swap file, but a file with the same name already exists and is still in use.
To disable and remove it, run the commands:
sudo swapoff -a sudo rm -f /swapfile
Managing Swap files on other Linuxes
To increase or create a swap file on other distributions, see the articles:
- How to create or enlarge a Swap file in Kali Linux
- Swap file and swap partition in Arch Linux (BlackArch): what to choose and how to add Swap
- Dynamic swap files are created only when needed
How to create a swap partition on another drive
You don't have to use the system disk for the swap, which can be low on space. You can create a partition on any drive in the system. For details, see the instruction “How to create a swap partition not on the system drive. How to move the swap partition to another disk”.
How to check swap file usage in Linux
Stress testing the system in a out of RAM scenario: How to check Swap file usage in Linux
Related articles:
- Swap file and swap partition in Arch Linux (BlackArch): what to choose and how to add Swap (97.2%)
- How to check Swap file usage in Linux (59.9%)
- Dynamic swap files are created only when needed (59.9%)
- What happens if Linux runs out of RAM. Do I need a Swap file (55.6%)
- What is the difference between Suspend and Hibernate in Linux. Why is the Hibernation button missing? (54%)
- Error “remote: Support for password authentication was removed on August 13, 2021. Please use a personal access token instead” (SOLVED) (RANDOM - 50%)