How to disable “did you mean…” feature in Linux shell
July 10, 2022
How to disable offers to install a package with an incorrectly entered command
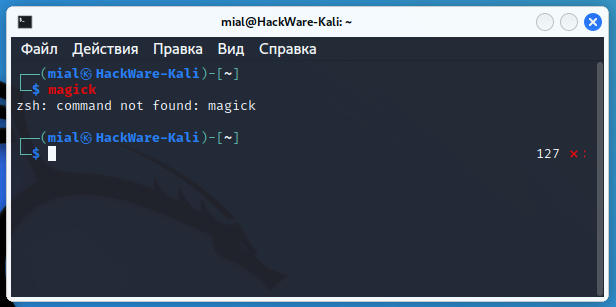
In case the command you entered into the Linux console is not found, some distributions show additional information suggesting which packages the entered command might be in and how it can be installed.
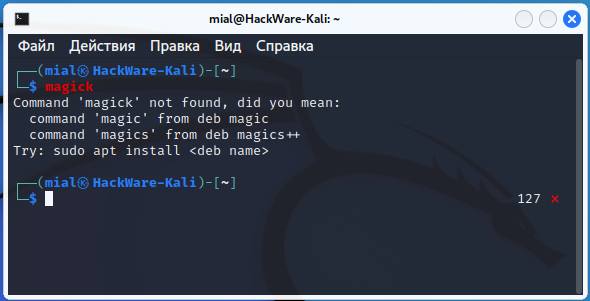
An example of such a message:
Command 'magick' not found, did you mean: command 'magic' from deb magic command 'magics' from deb magics++ Try: sudo apt install <deb name>
Distributions that use this are for example Kali Linux and Ubuntu.
If for some reason you do not like this behavior of the terminal, and you want the error output to be limited to the message “command not found”, then this article will tell you how to do it.
Since the “did you mean…” feature is provided by the “command-not-found” package, you can remove the package to disable it:
sudo apt remove command-not-found
After that, restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Solution for no errors appear after removing command-not-found
In order for the “command not found” messages to start showing again after removing command-not-found, restart your computer.
Disabling “did you mean…” feature without removing “command-not-found” package
This method can be used by a non-root user, that is, without the ability to remove packages.
Open file
- .bashrc (for Bash shell)
- .zshrc (for Zsh shell)
See also: How to find out which shell is in use in Linux
And add the line there
unset command_not_found_handle
Before adding the specified line to one of the shell files, check for lines that enable command-not-found. For example, in Kali Linux, the following lines are present:
# enable command-not-found if installed
if [ -f /etc/zsh_command_not_found ]; then
. /etc/zsh_command_not_found
fi
Delete or comment out these lines in the .zshrc file to get:
## enable command-not-found if installed #if [ -f /etc/zsh_command_not_found ]; then # . /etc/zsh_command_not_found #fi
As a result, the command-not-found feature will be disabled in all newly opened terminals.
Related articles:
- How to change the login shell in Linux. chsh instruction (92.3%)
- How to find out which shell is in use in Linux (92.3%)
- How to convert a string to uppercase in Bash (92.3%)
- How to convert a string to lowercase in Bash (92.3%)
- How to run small Python code in Bash (69.3%)
- Free analogue of Total Commander (RANDOM - 50%)