How to choose the default Java version in Arch Linux
February 18, 2021
Several versions of the JDK and OpenJDK are available in the standard Arch Linux repositories (and derivative distributions). You can install one or more of them. Even if you have the latest version installed, some programs may install a different version of the JDK as their dependency - multiple versions are allowed, they do not cause conflicts.
After that, you can see which of these versions is used by default, and also change it using the archlinux-java program.
Usage:
archlinux-java <COMMAND>
As a COMMAND it can be:
status List installed Java environments and enabled one get Return the short name of the Java environment set as default set <JAVA_ENV> Force <JAVA_ENV> as default unset Unset current default Java environment fix Fix an invalid/broken default Java environment configuration
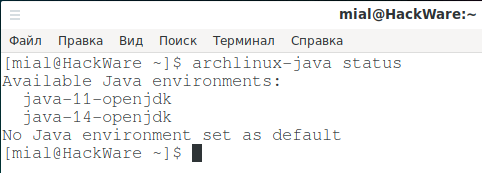
Start by viewing the status:
archlinux-java status
As you can see, I have two Java environments available
- java-11-openjdk
- java-14-openjdk
And no Java environment is selected as the default.
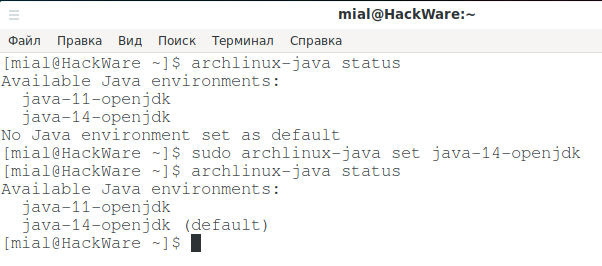
I set java-14-openjdk as my default environment:
sudo archlinux-java set java-14-openjdk
I check again:
archlinux-java status
As you can see, java-14-openjdk is now used - the word (default) indicates this.
Errors: command java, javac or javap not found
When trying to start one of the following programs, you may encounter errors:
java bash: java: command not found # OR bash: /usr/bin/java: No such file or directory javac bash: javac: command not found # OR bash: /usr/bin/javac: No such file or directory javap bash: javap: command not found # OR bash: /usr/bin/javap: No such file or directory
If you have already installed the JDK, then you need to select the version that will be used by default. This can be done using archlinux-java as shown above. After that, the error will disappear.
Related articles:
- Analogue of the --force option in pacman (100%)
- How to downgrade to a previous kernel in Arch Linux (100%)
- Error “Cannot load modules/libphp7.so” (SOLVED) (100%)
- pacman error “warning: failed to retrieve some files” (SOLVED) (100%)
- phpMyAdmin error “Error: Undefined constant "SODIUM_CRYPTO_SECRETBOX_KEYBYTES"” (SOLVED) (100%)
- Is it safe to remove configuration files left over from removed packages? (SOLVED) (RANDOM - 57.5%)