How to Run a Program Automatically on Startup in Linux
February 24, 2021
If you want a program or script to run when the system starts up, then this can be done using systemctl. This method is universal: autorun also works on headless servers, not just when you enter a graphical desktop environment. This method is universal and will work on all systems where systemctl is present (e.g. Debian, Linux Mint, Ubuntu, Kali Linux, Arch Linux, etc.).
To add a script to autoload in Linux, you need to create a specific file in the /etc/systemd/system/ directory. Choose your own file name. For example, I want to run a script on startup that contains several rules to hinder DOS attacks. This file is located at /root/firewall.sh
We start by assigning the correct permissions to the file:
chmod 755 /root/firewall.sh
Make sure the file has shebang #!/bin/bash (or whatever matches the contents of the file).
I create a file anti-dos.service (you can choose your own name):
vim /etc/systemd/system/anti-dos.service
Content of my file
[Unit] Description=Initial anti-DOS protection. [Service] ExecStart=/root/firewall.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Here
- Description=Initial anti-DOS protection. - this is a description, replace the description with your own.
- ExecStart=/root/firewall.sh - full path to the file that I want to add to startup is specified.
Don't write something like “ExecStart=/bin/sh /path/to/script.sh” as that won't work. If you really want to specify an interpreter and a script, then use a construction like this:
/usr/bin/bash -c 'INTERPRETER /PATH/TO/SCRIPT'
For instance:
/usr/bin/bash -c 'php /root/bin/translator.php'
Example file using this construction
[Unit] Description=Launch translator. [Service] ExecStart=/usr/bin/bash -c 'php /root/bin/translator.php' [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
- WantedBy=multi-user.target - means that autorun is made for all users.
To start the services in the current session (change the name anti-dos.service to the name of your file):
systemctl start anti-dos.service
To check the status of a service:
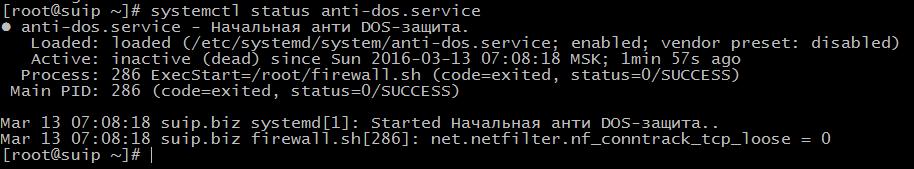
systemctl status anti-dos.service
To enable autostart, you need to do this (change the name anti-dos.service to the name of your file):
systemctl enable anti-dos.service
Creating a link says that adding to autostart worked:
Let's restart the server to check))
The screenshot above shows that everything worked properly. The fact that the process is shown as deceased, in my case, is normal. Since I added not a service to autostart, but a one-time script.
To make sure that the firewall settings are in effect, I type:
iptables --list
Yes, my firewall rules are there.
You can also find your autorun file in the list of everything added to startup:
systemctl list-unit-files
After editing files with the extension .service, for the changes to take effect, you need to run the command:
systemctl daemon-reload
Related articles:
- How to install PowerShell in Linux Mint (77.3%)
- How to install PowerShell on Arch Linux, Manjaro, BlackArch (77.3%)
- Xfce boots without Taskbar and Start button (SOLVED) (77.3%)
- How to change the default operating system in Arch Linux (for UEFI and systemd-boot) (72.8%)
- Error “Failed to talk to init daemon” (SOLVED) (72.8%)
- Warning: apt-key is deprecated (SOLVED) (RANDOM - 50%)