Tag: mount
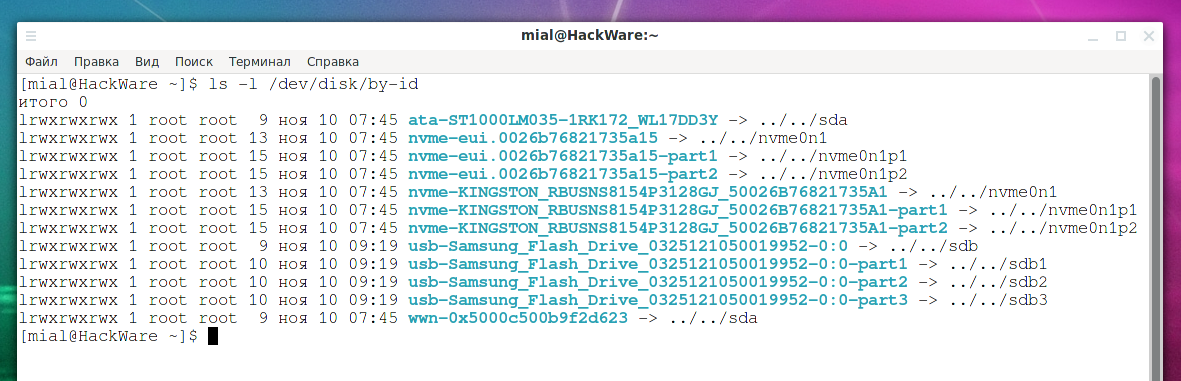
Persistent names for block devices
Posted by Alex On November 10, 2021

An unplugged disk causes a delay in system boot
Posted by Alex On July 15, 2021
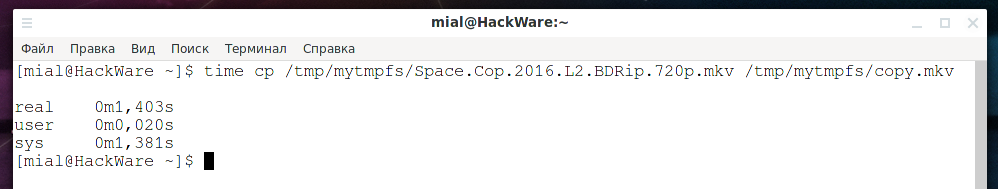
The in-memory file system - how to use tmpfs
Posted by Alex On February 19, 2021