Tag: mounting disks
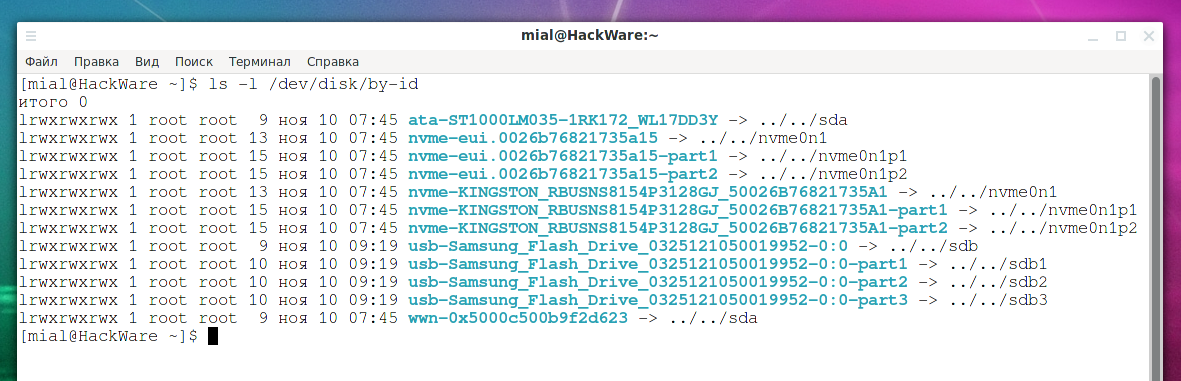
Persistent names for block devices
Posted by Alex On November 10, 2021

How to repair an LVM disk using fsck
Posted by Alex On November 1, 2021

How to determine why Linux boots into Emergency mode
Posted by Alex On November 1, 2021

An unplugged disk causes a delay in system boot
Posted by Alex On July 15, 2021