Tag: pikaur

Error: failed to commit transaction (conflicting files) (SOLVED)
Posted by Alex On September 24, 2023

Error “TypeError: ‘AURPackageInfo’ does not have attribute ‘submitter’” (SOLVED)
Posted by Alex On December 5, 2022

How to download a package without installation in Arch Linux and Manjaro. How to download the AUR package source code
Posted by Alex On May 22, 2022

How to view package information in Arch Linux (BlackArch, Manjaro)
Posted by Alex On February 18, 2021
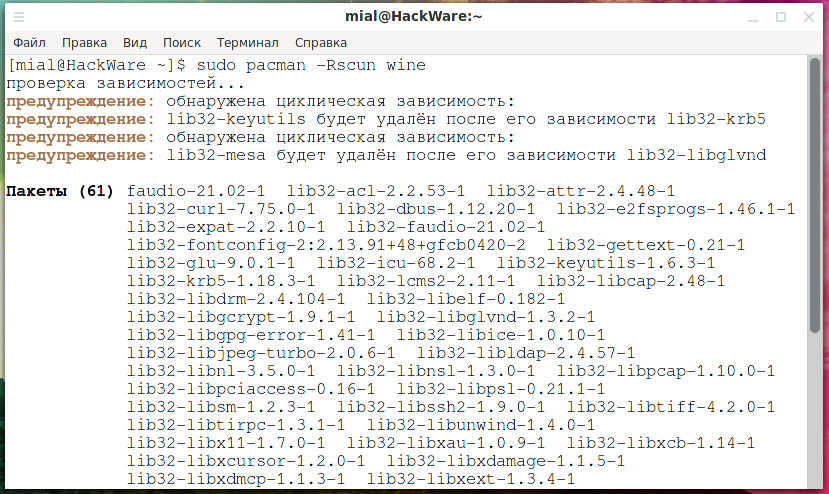
How to completely uninstall a package along with dependencies on Arch Linux (as well as BlackArch and Manjaro)
Posted by Alex On February 18, 2021