Tag: RAM

What happens if Linux runs out of RAM. Do I need a Swap file
Posted by Alex On November 20, 2021

How to use ps command to monitor Linux processes
Posted by Alex On October 30, 2021

htop command guide: how to view processes in Linux interactively
Posted by Alex On October 17, 2021

How to use the top command to monitor Linux processes
Posted by Alex On October 17, 2021
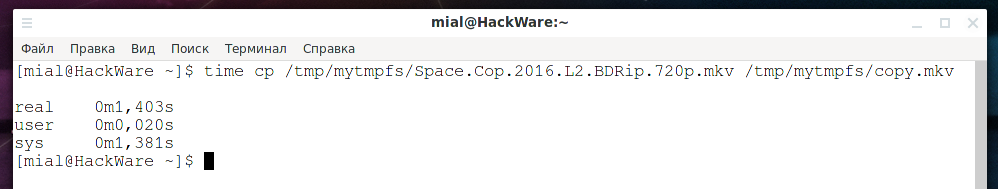
The in-memory file system - how to use tmpfs
Posted by Alex On February 19, 2021